mirror of
https://github.com/tj/n.git
synced 2024-11-25 07:39:21 +01:00
198 lines
7.7 KiB
Markdown
198 lines
7.7 KiB
Markdown
# `n` – Interactively Manage Your Node.js Versions
|
||
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
|
||
Node.js version management: no subshells, no profile setup, no convoluted API, just **simple**.
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
(Note: `n` is not supported natively on Windows.)
|
||
|
||
- [`n` – Interactively Manage Your Node.js Versions](#n-%E2%80%93-Interactively-Manage-Your-Nodejs-Versions)
|
||
- [Installation](#Installation)
|
||
- [Third Party Installers](#Third-Party-Installers)
|
||
- [Installing/Activating Node Versions](#InstallingActivating-Node-Versions)
|
||
- [Removing Versions](#Removing-Versions)
|
||
- [Binary Usage](#Binary-Usage)
|
||
- [Help](#Help)
|
||
- [Custom Source](#Custom-Source)
|
||
- [Custom Architecture](#Custom-Architecture)
|
||
- [Optional Environment Variables](#Optional-Environment-Variables)
|
||
|
||
## Installation
|
||
|
||
Since you probably already have `node`, the easiest way to install `n` is through `npm`:
|
||
|
||
npm install -g n
|
||
|
||
Alternatively, you can clone this repo and
|
||
|
||
make install
|
||
|
||
to install `n` to `bin/n` of the directory specified in the environment variable `$PREFIX`, which defaults to `/usr/local` (note that you will likely need to use `sudo`). To install `n` in a custom location (such as `$CUSTOM_LOCATION/bin/n`), run `PREFIX=$CUSTOM_LOCATION make install`.
|
||
|
||
Once installed, `n` caches `node` versions in subdirectory `n/versions` of the directory specified in environment variable `N_PREFIX`, which defaults to `/usr/local`; and the _active_ `node` version is installed directly in `N_PREFIX`.
|
||
|
||
To avoid requiring `sudo` for `n` and `npm` global installs, it is recommended you either install to your home directory using `N_PREFIX`, or take ownership of the system directories:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
# make cache folder (if missing) and take ownership
|
||
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/n
|
||
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/n
|
||
# take ownership of node install destination folders
|
||
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/bin /usr/local/lib /usr/local/include /usr/local/share
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Third Party Installers
|
||
|
||
On macOS with [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) you can install the [n formula](https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew-core/blob/master/Formula/n.rb).
|
||
|
||
brew install n
|
||
|
||
On Linux and macOS, [n-install](https://github.com/mklement0/n-install) allows installation directly from GitHub; for instance:
|
||
|
||
curl -L https://git.io/n-install | bash
|
||
|
||
n-install sets both `PREFIX` and `N_PREFIX` to `$HOME/n`, installs `n` to `$HOME/n/bin`, modifies the initialization files of supported shells to export `N_PREFIX` and add `$HOME/n/bin` to the `PATH`, and installs the latest LTS `node` version.
|
||
|
||
As a result, both `n` itself and all `node` versions it manages are hosted inside a single, optionally configurable directory, which you can later remove with the included `n-uninstall` script. `n-update` updates `n` itself to the latest version. See the [n-install repo](https://github.com/mklement0/n-install) for more details.
|
||
|
||
## Installing/Activating Node Versions
|
||
|
||
Simply execute `n <version>` to install a version of `node`. If `<version>` has already been installed (via `n`), `n` will activate that version.
|
||
A leading `v` is optional, and a partial version number installs the newest matching version.
|
||
|
||
n 4.9.1
|
||
n 10
|
||
n v8.11.3
|
||
|
||
Execute `n` on its own to view your currently installed versions. Use the up and down arrow keys to navigate and press enter to select. Use `q` or ^C (control + C) to exit the selection screen.
|
||
If you like vim key bindings during the selection of node versions, you can use `j` and `k` to navigate up or down without using arrows.
|
||
|
||
$ n
|
||
|
||
node/4.9.1
|
||
ο node/8.11.3
|
||
node/10.15.0
|
||
|
||
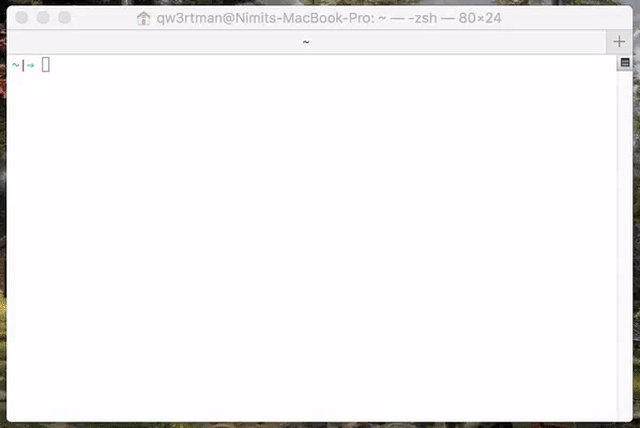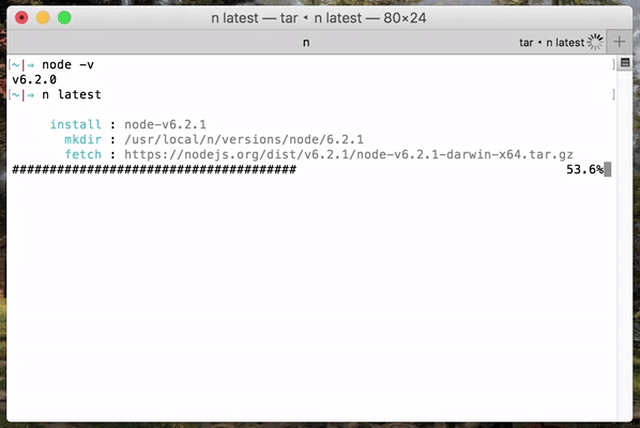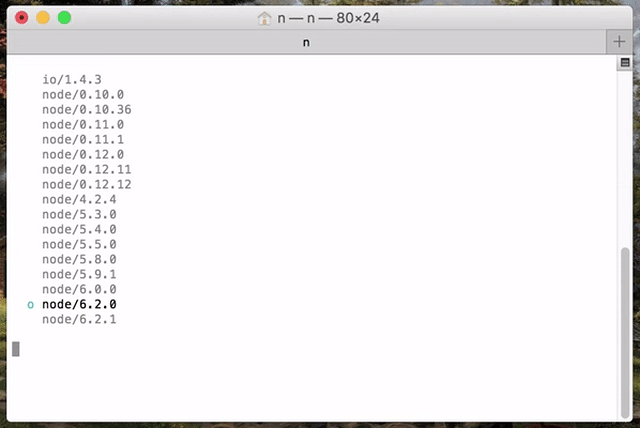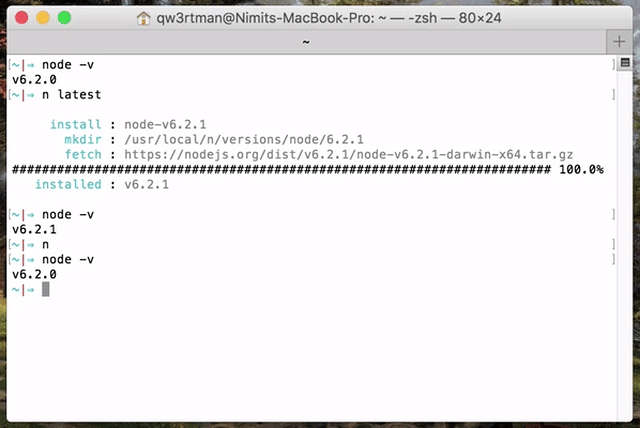
Use or install the latest official release:
|
||
|
||
n latest
|
||
|
||
Use or install the latest LTS official release:
|
||
|
||
n lts
|
||
|
||
(If the active node version does not change after install, try opening a new shell in case seeing a stale version.)
|
||
|
||
## Removing Versions
|
||
|
||
Remove some cached versions:
|
||
|
||
n rm 0.9.4 v0.10.0
|
||
|
||
Removing all cached versions except the current version:
|
||
|
||
n prune
|
||
|
||
Remove the installed node and npm (does not affect the cached version). This can be useful
|
||
to revert to the system version of node (if in a different location), or if you no longer
|
||
wish to use node and npm, or are switching to a different way of managing them.
|
||
|
||
n uninstall
|
||
|
||
## Binary Usage
|
||
|
||
When running multiple versions of `node`, we can target
|
||
them directly by asking `n` for the binary path:
|
||
|
||
$ n bin 0.9.4
|
||
/usr/local/n/versions/0.9.4/bin/node
|
||
|
||
Or by using a specific version through `n`'s `use` sub-command:
|
||
|
||
n use 0.9.4 some.js
|
||
|
||
Flags also work here:
|
||
|
||
n as 0.9.4 --debug some.js
|
||
|
||
## Help
|
||
|
||
Output can also be obtained from `n --help`.
|
||
|
||
Usage: n [options/env] [COMMAND] [args]
|
||
|
||
Environments:
|
||
n [COMMAND] [args] Uses default env (node)
|
||
|
||
Commands:
|
||
|
||
n Output versions installed
|
||
n latest Install or activate the latest node release
|
||
n -a x86 latest As above but force 32 bit architecture
|
||
n lts Install or activate the latest LTS node release
|
||
n <version> Install node <version>
|
||
n use <version> [args ...] Execute node <version> with [args ...]
|
||
n bin <version> Output bin path for <version>
|
||
n rm <version ...> Remove the given version(s)
|
||
n prune Remove all versions except the active version
|
||
n --latest Output the latest node version available
|
||
n --lts Output the latest LTS node version available
|
||
n ls Output the versions of node available
|
||
|
||
Options:
|
||
|
||
-V, --version Output version of n
|
||
-h, --help Display help information
|
||
-q, --quiet Disable curl output (if available)
|
||
-d, --download Download only
|
||
-a, --arch Override system architecture
|
||
|
||
Aliases:
|
||
|
||
which bin
|
||
use as
|
||
list ls
|
||
- rm
|
||
stable lts
|
||
|
||
## Custom Source
|
||
|
||
If you would like to use a different node mirror which has the same layout as the default <https://nodejs.org/dist/>, you can define `NODE_MIRROR`.
|
||
The most common example is users in China can define:
|
||
|
||
export NODE_MIRROR=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node
|
||
|
||
## Custom Architecture
|
||
|
||
By default `n` picks the binaries matching your system architecture, e.g. `n` will download 64 bit binaries for a 64 bit system. You can override this by using the `-a` or `--arch` option.
|
||
|
||
Download and use latest 32 bit version of `node`:
|
||
|
||
n --arch x86 latest
|
||
|
||
Download and use 64 bit LTS version of `node` for older Mac Intel Core 2 Duo systems (x86 image is no longer available but x64 runs fine):
|
||
|
||
n --arch x64 lts
|
||
|
||
## Optional Environment Variables
|
||
|
||
The `n` command downloads and installs to `/usr/local` by default, but you may override this location by defining `N_PREFIX`.
|
||
To change the location to say `$HOME/.n`, add lines like the following to your shell initialization file:
|
||
|
||
export N_PREFIX=$HOME/.n
|
||
export PATH=$N_PREFIX/bin:$PATH
|
||
|
||
By default `n` downloads archives from the mirror site which have been compressed with `gzip`. You can switch to using the `xz` compressed archives by defining `N_USE_XZ`.
|
||
|
||
export N_USE_XZ=true
|
||
|
||
In brief:
|
||
|
||
- `NODE_MIRROR`: See [Custom source](#custom-source)
|
||
- support for [NO_COLOR](http://no-color.org) and [CLICOLOR=0](https://bixense.com/clicolors) for controlling use of ANSI color codes
|