mirror of
https://github.com/tj/n.git
synced 2024-11-24 19:46:56 +01:00
290 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
290 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
# `n` – Interactively Manage Your Node.js Versions
|
||
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/n)
|
||
|
||
Node.js version management: no subshells, no profile setup, no convoluted API, just **simple**.
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
- [`n` – Interactively Manage Your Node.js Versions](#n--interactively-manage-your-nodejs-versions)
|
||
- [Supported Platforms](#supported-platforms)
|
||
- [Installation](#installation)
|
||
- [Third Party Installers](#third-party-installers)
|
||
- [Installing Node.js Versions](#installing-nodejs-versions)
|
||
- [Specifying Node.js Versions](#specifying-nodejs-versions)
|
||
- [Removing Versions](#removing-versions)
|
||
- [Using Downloaded Node.js Versions Without Reinstalling](#using-downloaded-nodejs-versions-without-reinstalling)
|
||
- [Preserving npm](#preserving-npm)
|
||
- [Miscellaneous](#miscellaneous)
|
||
- [Custom Source](#custom-source)
|
||
- [Custom Architecture](#custom-architecture)
|
||
- [Optional Environment Variables](#optional-environment-variables)
|
||
- [How It Works](#how-it-works)
|
||
|
||
## Supported Platforms
|
||
|
||
`n` is supported on macOS, Linux, including with Windows Subsystem for Linux, and various other unix-like systems.
|
||
It is written as a BASH script but does not require you to use BASH as your command shell.
|
||
|
||
`n` does not work in native shells on Microsoft Windows (like PowerShell), or Git for Windows BASH, or with the Cygwin DLL.
|
||
|
||
## Installation
|
||
|
||
If you already have Node.js installed, an easy way to install `n` is using `npm`:
|
||
|
||
npm install -g n
|
||
|
||
The `n` command downloads and installs to `/usr/local` by default, but you may override this location by defining `N_PREFIX`.
|
||
`n` caches Node.js versions in subdirectory `n/versions`. The _active_ Node.js version is installed in subdirectories `bin`, `include`, `lib`, and `share`.
|
||
|
||
To avoid requiring `sudo` for `n` and `npm` global installs, it is suggested you either install to your home directory using `N_PREFIX`, or take ownership of the system directories:
|
||
|
||
# make cache folder (if missing) and take ownership
|
||
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/n
|
||
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/n
|
||
# make sure the required folders exist (safe to execute even if they already exist)
|
||
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin /usr/local/lib /usr/local/include /usr/local/share
|
||
# take ownership of Node.js install destination folders
|
||
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/bin /usr/local/lib /usr/local/include /usr/local/share
|
||
|
||
-----
|
||
|
||
If `npm` is not yet available, one way to bootstrap an install is to download and run `n` directly. To install the `lts` version of Node.js:
|
||
|
||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tj/n/master/bin/n | bash -s lts
|
||
# If you want n installed, you can use npm now.
|
||
npm install -g n
|
||
|
||
Alternatively, you can clone this repo and
|
||
|
||
make install
|
||
|
||
to install `n` to `bin/n` of the directory specified in the environment variable `$PREFIX`, which defaults to `/usr/local` (note that you will likely need to use `sudo`). To install `n` in a custom location (such as `$CUSTOM_LOCATION/bin/n`), run `PREFIX=$CUSTOM_LOCATION make install`.
|
||
|
||
### Third Party Installers
|
||
|
||
On macOS with [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) you can install the [n formula](https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew-core/blob/master/Formula/n/n.rb).
|
||
|
||
brew install n
|
||
|
||
Or on macOS with [MacPorts](https://www.macports.org/) you can install the [n port](https://ports.macports.org/port/n/summary):
|
||
|
||
port install n
|
||
|
||
On Linux and macOS, [n-install](https://github.com/mklement0/n-install) allows installation directly from GitHub; for instance:
|
||
|
||
curl -L https://bit.ly/n-install | bash
|
||
|
||
n-install sets both `PREFIX` and `N_PREFIX` to `$HOME/n`, installs `n` to `$HOME/n/bin`, modifies the initialization files of supported shells to export `N_PREFIX` and add `$HOME/n/bin` to the `PATH`, and installs the latest LTS Node.js version.
|
||
|
||
As a result, both `n` itself and all Node.js versions it manages are hosted inside a single, optionally configurable directory, which you can later remove with the included `n-uninstall` script. `n-update` updates `n` itself to the latest version. See the [n-install repo](https://github.com/mklement0/n-install) for more details.
|
||
|
||
## Installing Node.js Versions
|
||
|
||
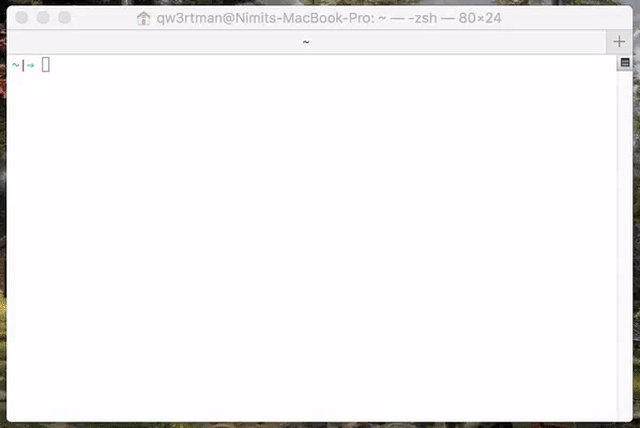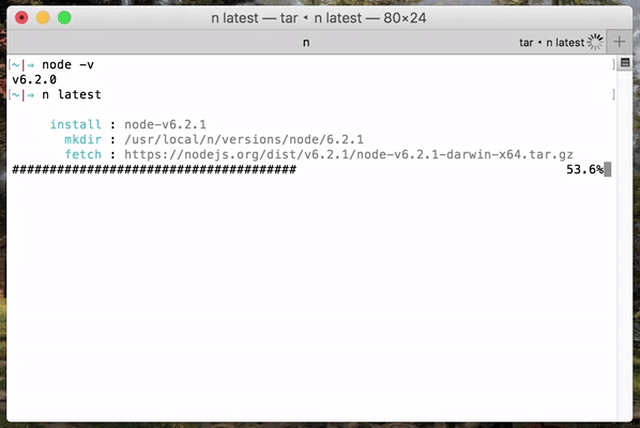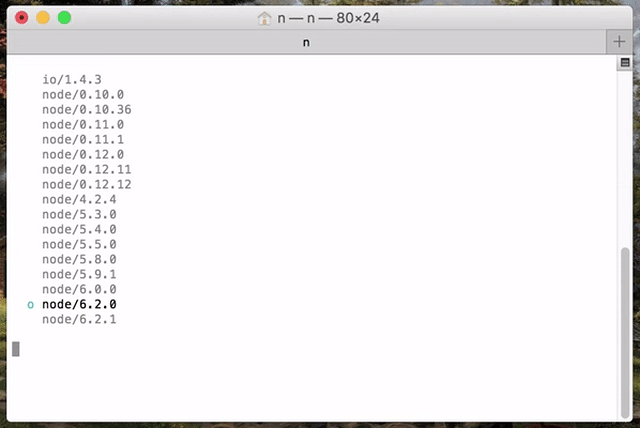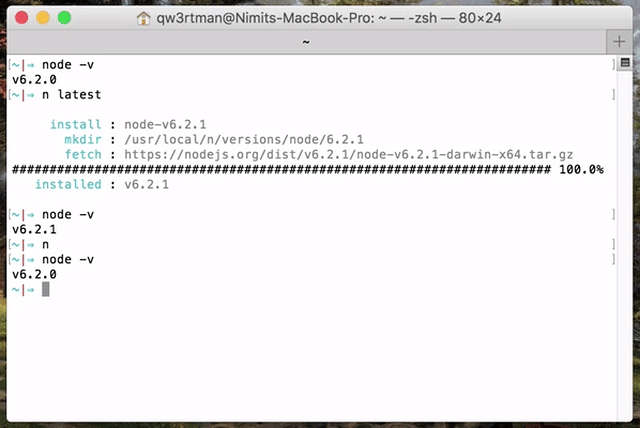
Simply execute `n <version>` to download and install a version of Node.js. If `<version>` has already been downloaded, `n` will install from its cache.
|
||
|
||
n 10.16.0
|
||
n lts
|
||
|
||
Execute `n` on its own to view your downloaded versions, and install the selected version.
|
||
|
||
$ n
|
||
|
||
node/4.9.1
|
||
ο node/8.11.3
|
||
node/10.15.0
|
||
|
||
Use up/down arrow keys to select a version, return key to install, d to delete, q to quit
|
||
|
||
(You can also use <kbd>j</kbd> and <kbd>k</kbd> to select next or previous version instead of using arrows, or <kbd>ctrl+n</kbd> and <kbd>ctrl+p</kbd>.)
|
||
|
||
If the active node version does not change after install, try opening a new shell in case seeing a stale version.
|
||
|
||
## Specifying Node.js Versions
|
||
|
||
There are a variety of ways of specifying the target Node.js version for `n` commands. Most commands use the latest matching version, and `n ls-remote` lists multiple matching versions.
|
||
|
||
Numeric version numbers can be complete or incomplete, with an optional leading `v`.
|
||
|
||
- `4.9.1`
|
||
- `8`: 8.x.y versions
|
||
- `v6.1`: 6.1.x versions
|
||
|
||
There are labels for two especially useful versions:
|
||
|
||
- `lts`: newest Long Term Support official release
|
||
- `latest`, `current`: newest official release
|
||
|
||
There is an `auto` label to read the target version from a file in the current directory, or any parent directory. `n` looks for in order:
|
||
|
||
- `.n-node-version`: version on single line. Custom to `n`.
|
||
- `.node-version`: version on single line. Used by multiple tools: [node-version-usage](https://github.com/shadowspawn/node-version-usage)
|
||
- `.nvmrc`: version on single line. Used by `nvm`.
|
||
- if no version file found, look for `engine` as below.
|
||
|
||
The `engine` label looks for a `package.json` file and reads the `engines` field to determine compatible Node.js. Requires an installed version of `node`, and uses `npx semver` to resolve complex ranges.
|
||
|
||
There is support for the named release streams:
|
||
|
||
- `argon`, `boron`, `carbon`: codenames for LTS release streams
|
||
|
||
These Node.js support aliases may be used, although simply resolve to the latest matching version:
|
||
|
||
- `active`, `lts_active`, `lts_latest`, `lts`, `current`, `supported`
|
||
|
||
The last version form is for specifying [other releases](https://nodejs.org/download) available using the name of the remote download folder optionally followed by the complete or incomplete version.
|
||
|
||
- `nightly`
|
||
- `test/v11.0.0-test20180528`
|
||
- `rc/10`
|
||
|
||
## Removing Versions
|
||
|
||
Remove some cached versions:
|
||
|
||
n rm 0.9.4 v0.10.0
|
||
|
||
Removing all cached versions except the installed version:
|
||
|
||
n prune
|
||
|
||
Remove the installed Node.js (does not affect the cached versions). This can be useful
|
||
to revert to the system version of node (if in a different location), or if you no longer
|
||
wish to use node and npm, or are switching to a different way of managing them.
|
||
|
||
n uninstall
|
||
|
||
## Using Downloaded Node.js Versions Without Reinstalling
|
||
|
||
There are three commands for working directly with your downloaded versions of Node.js, without reinstalling.
|
||
|
||
You can show the path to the downloaded `node` version:
|
||
|
||
$ n which 6.14.3
|
||
/usr/local/n/versions/6.14.3/bin/node
|
||
|
||
Or run a downloaded `node` version with the `n run` command:
|
||
|
||
n run 8.11.3 --debug some.js
|
||
|
||
Or execute a command with `PATH` modified so `node` and `npm` will be from the downloaded Node.js version.
|
||
(NB: `npm` run this way will be using global node_modules from the target node version folder.)
|
||
|
||
n exec 10 my-script --fast test
|
||
n exec lts zsh
|
||
|
||
## Preserving npm
|
||
|
||
A Node.js install normally also includes `npm`, `npx`, and `corepack`, but you may wish to preserve your current (especially newer) versions using `--preserve`:
|
||
|
||
$ npm install -g npm@latest
|
||
...
|
||
$ npm --version
|
||
6.13.7
|
||
# Node.js 8.17.0 includes (older) npm 6.13.4
|
||
$ n -p 8
|
||
installed : v8.17.0
|
||
$ npm --version
|
||
6.13.7
|
||
|
||
You can make this the default by setting the environment variable to a non-empty string. There are separate environment variables for `npm` and `corepack`:
|
||
|
||
export N_PRESERVE_NPM=1
|
||
export N_PRESERVE_COREPACK=1
|
||
|
||
You can be explicit to get the desired behaviour whatever the environment variables:
|
||
|
||
n --preserve nightly
|
||
n --no-preserve latest
|
||
|
||
## Miscellaneous
|
||
|
||
Command line help can be obtained from `n --help`.
|
||
|
||
List matching remote versions available for download:
|
||
|
||
n ls-remote lts
|
||
n ls-remote latest
|
||
n lsr 10
|
||
n --all lsr
|
||
|
||
List downloaded versions in cache:
|
||
|
||
n ls
|
||
|
||
Display diagnostics to help resolve problems:
|
||
|
||
n doctor
|
||
|
||
## Custom Source
|
||
|
||
If you would like to use a different Node.js mirror which has the same layout as the default <https://nodejs.org/dist/>, you can define `N_NODE_MIRROR`.
|
||
The most common example is from users in China who can define:
|
||
|
||
export N_NODE_MIRROR=https://npmmirror.com/mirrors/node
|
||
|
||
If the custom mirror requires authentication you can add the [url-encoded](https://urlencode.org) username and password into the URL. e.g.
|
||
|
||
export N_NODE_MIRROR=https://encoded-username:encoded-password@host:port/path
|
||
|
||
There is also `N_NODE_DOWNLOAD_MIRROR` for a different mirror with same layout as the default <https://nodejs.org/download>.
|
||
|
||
## Custom Architecture
|
||
|
||
By default `n` picks the binaries matching your system architecture. For example, on a 64 bit system `n` will download 64 bit binaries.
|
||
|
||
On a Mac with Apple silicon:
|
||
|
||
- for Node.js 16 and higher, `n` defaults to arm64 binaries which run natively
|
||
- for older versions of Node.js, `n` defaults to x64 binaries which run in Rosetta 2
|
||
|
||
You can override the default architecture by using the `-a` or `--arch` option.
|
||
|
||
e.g. reinstall latest version of Node.js with x64 binaries:
|
||
|
||
n rm current
|
||
n --arch x64 current
|
||
|
||
## Optional Environment Variables
|
||
|
||
The `n` command downloads and installs to `/usr/local` by default, but you may override this location by defining `N_PREFIX`.
|
||
To change the location to say `$HOME/.n`, add lines like the following to your shell initialization file:
|
||
|
||
export N_PREFIX=$HOME/.n
|
||
export PATH=$N_PREFIX/bin:$PATH
|
||
|
||
If you want to store the downloads under a different location, use `N_CACHE_PREFIX`. This does *not* affect the currently active
|
||
node version.
|
||
|
||
`n` defaults to using xz compressed Node.js tarballs for the download if it is likely tar on the system supports xz decompression.
|
||
You can override the automatic choice by setting an environment variable to zero or non-zero:
|
||
|
||
export N_USE_XZ=0 # to disable
|
||
export N_USE_XZ=1 # to enable
|
||
|
||
You can be explicit to get the desired behaviour whatever the environment variable:
|
||
|
||
n install --use-xz nightly
|
||
n install --no-use-xz latest
|
||
|
||
In brief:
|
||
|
||
- `N_NODE_MIRROR`: See [Custom source](#custom-source)
|
||
- `N_NODE_DOWNLOAD_MIRROR`: See [Custom source](#custom-source)
|
||
- support for [NO_COLOR](https://no-color.org) and [CLICOLOR=0](https://bixense.com/clicolors) for controlling use of ANSI color codes
|
||
- `N_MAX_REMOTE_MATCHES` to change the default `ls-remote` maximum of 20 matching versions
|
||
- `N_PRESERVE_NPM`: See [Preserving npm](#preserving-npm)
|
||
- `N_PRESERVE_COREPACK`: See [Preserving npm](#preserving-npm)
|
||
|
||
## How It Works
|
||
|
||
`n` downloads a prebuilt Node.js package and installs to a single prefix (e.g. `/usr/local`). This overwrites the previous version. The `bin` folder in this location should be in your `PATH` (e.g. `/usr/local/bin`).
|
||
|
||
The downloads are kept in a cache folder to be used for reinstalls. The downloads are also available for limited use using `n which` and `n run` and `n exec`.
|
||
|
||
The global `npm` packages are not changed by the install, with the
|
||
exception of `npm` itself which is part of the Node.js install.
|