# Hono
[](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/actions)
[](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono)
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono)
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/hono)
[](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/pulse)
[](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/commits/master)
Hono[炎] - _**means flame🔥 in Japanese**_ - is small, simple, and ultrafast web framework for Service Worker based serverless applications like Cloudflare Workers and Fastly Compute@Edge.
```js
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hono!!'))
app.fire()
```
## Features
- **Ultrafast** - the router does not use linear loops.
- **Zero-dependencies** - using only Web standard API.
- **Middleware** - builtin middleware and your own middleware.
- **Optimized** - for Cloudflare Workers.
## Benchmark
**Hono is fastest** compared to other routers for Cloudflare Workers.
```plain
hono x 779,197 ops/sec ±6.55% (78 runs sampled)
itty-router x 161,813 ops/sec ±3.87% (87 runs sampled)
sunder x 334,096 ops/sec ±1.33% (93 runs sampled)
worktop x 212,661 ops/sec ±4.40% (81 runs sampled)
Fastest is hono
✨ Done in 58.29s.
```
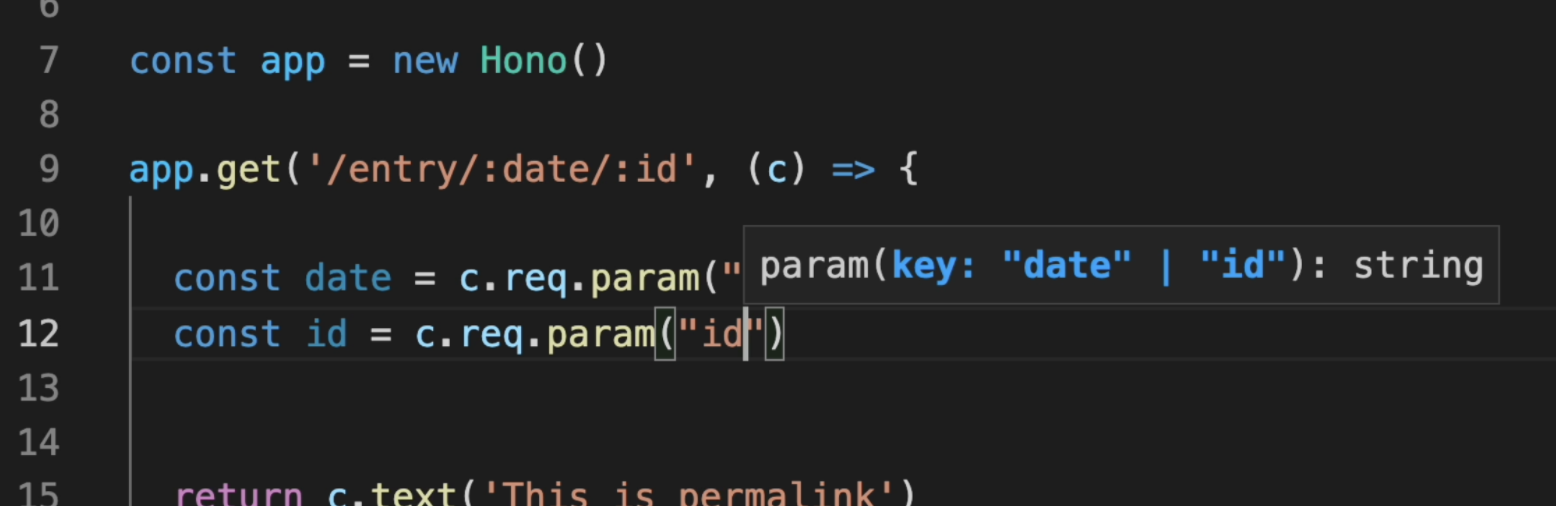
## Hono in 1 minute
A demonstration to create an application of Cloudflare Workers with Hono.
Now, the named path parameter has types.
## Install
You can install Hono from the npm registry.
```sh
$ yarn add hono
```
or
```sh
$ npm install hono
```
## Methods
An instance of `Hono` has these methods.
- app.**HTTP_METHOD**(path, handler)
- app.**all**(path, handler)
- app.**route**(path)
- app.**use**(path, middleware)
- app.**fire**()
- app.**fetch**(request, env, event)
## Routing
### Basic
```js
// HTTP Methods
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('GET /'))
app.post('/', (c) => c.text('POST /'))
// Wildcard
app.get('/wild/*/card', (c) => {
return c.text('GET /wild/*/card')
})
// Any HTTP methods
app.all('/hello', (c) => c.text('Any Method /hello'))
```
### Named Parameter
```js
app.get('/user/:name', (c) => {
const name = c.req.param('name')
...
})
```
### Regexp
```js
app.get('/post/:date{[0-9]+}/:title{[a-z]+}', (c) => {
const date = c.req.param('date')
const title = c.req.param('title')
...
})
```
### Nested route
```js
const book = app.route('/book')
book.get('/', (c) => c.text('List Books')) // GET /book
book.get('/:id', (c) => {
// GET /book/:id
const id = c.req.param('id')
return c.text('Get Book: ' + id)
})
book.post('/', (c) => c.text('Create Book')) // POST /book
```
### no strict
If `strict` is set `false`, `/hello`and`/hello/` are treated the same. Default is `true`.
```js
const app = new Hono({ strict: false })
app.get('/hello', (c) => c.text('/hello or /hello/'))
```
### async/await
```js
app.get('/fetch-url', async (c) => {
const response = await fetch('https://example.com/')
return c.text(`Status is ${response.status}`)
})
```
## Middleware
### Builtin Middleware
```js
import { Hono } from 'hono'
import { poweredBy } from 'hono/powered-by'
import { logger } from 'hono/logger'
import { basicAuth } from 'hono/basicAuth'
const app = new Hono()
app.use('*', poweredBy())
app.use('*', logger())
app.use(
'/auth/*',
basicAuth({
username: 'hono',
password: 'acoolproject',
})
)
```
Available builtin middleware are listed on [src/middleware](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/tree/master/src/middleware).
### Custom Middleware
You can write your own middleware.
```js
// Custom logger
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
console.log(`[${c.req.method}] ${c.req.url}`)
await next()
})
// Add a custom header
app.use('/message/*', async (c, next) => {
await next()
await c.header('x-message', 'This is middleware!')
})
app.get('/message/hello', (c) => c.text('Hello Middleware!'))
```
## Context
To handle Request and Reponse, you can use Context object.
### c.req
```js
// Get Request object
app.get('/hello', (c) => {
const userAgent = c.req.headers.get('User-Agent')
...
})
// Shortcut to get a header value
app.get('/shortcut', (c) => {
const userAgent = c.req.header('User-Agent')
...
})
// Query params
app.get('/search', (c) => {
const query = c.req.query('q')
...
})
// Captured params
app.get('/entry/:id', (c) => {
const id = c.req.param('id')
...
})
```
### Shortcuts for Response
```js
app.get('/welcome', (c) => {
c.header('X-Message', 'Hello!')
c.header('Content-Type', 'text/plain')
c.status(201)
return c.body('Thank you for comming')
})
```
The Response is the same as below.
```js
new Response('Thank you for comming', {
status: 201,
statusText: 'Created',
headers: {
'X-Message': 'Hello',
'Content-Type': 'text/plain',
'Content-Length': '22',
},
})
```
### c.text()
Render texts as `Content-Type:text/plain`.
```js
app.get('/say', (c) => {
return c.text('Hello!')
})
```
### c.json()
Render JSON as `Content-Type:application/json`.
```js
app.get('/api', (c) => {
return c.json({ message: 'Hello!' })
})
```
### c.html()
Render HTML as `Content-Type:text/html`.
```js
app.get('/', (c) => {
return c.html('Hello! Hono!
')
})
```
### c.notFound()
Return the default `404 Not Found` Response.
```js
app.get('/notfound', (c) => {
return c.notFound()
})
```
### c.redirect()
Redirect, default status code is `302`.
```js
app.get('/redirect', (c) => c.redirect('/'))
app.get('/redirect-permanently', (c) => c.redirect('/', 301))
```
### c.res
```js
// Response object
app.use('/', (c, next) => {
next()
c.res.headers.append('X-Debug', 'Debug message')
})
```
### c.event
```js
// FetchEvent object
app.use('*', async (c, next) => {
c.event.waitUntil(
...
)
await next()
})
```
### c.env
```js
// Environment object for Cloudflare Workers
app.get('*', async c => {
const counter = c.env.COUNTER
...
})
```
## Not Found
You can write the default `404 Not Found` Response.
```js
app.notFound = (c) => {
return c.text('This is default 404 Not Found', 404)
}
```
## Error handling
You can handle errors in your way.
```js
app.onError = (err, c) => {
return c.text(`This is error message: ${err.mssage}`, 500)
}
```
## fire
`app.fire()` do this.
```js
addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(this.handleEvent(event))
})
```
## fetch
`app.fetch()` is for Cloudflare Module Worker syntax.
```js
export default {
fetch(request: Request, env: Env, event: FetchEvent) {
return app.fetch(request, env, event)
},
}
/*
or just do:
export default app
*/
```
## Cloudflare Workers with Hono
Using `wrangler` or `miniflare`, you can develop the application locally and publish it with few commands.
Let's write your first code for Cloudflare Workers with Hono.
### 1. Install Wrangler
Install Cloudflare Command Line "[Wrangler](https://github.com/cloudflare/wrangler)".
```sh
$ npm i @cloudflare/wrangler -g
```
### 2. `npm init`
Make a npm skeleton directory.
```sh
mkdir hono-example
cd hono-example
npm init -y
```
### 3. `wrangler init`
Init as a wrangler project.
```sh
$ wrangler init
```
### 4. `npm install hono`
Install `hono` from the npm registry.
```sh
$ npm i hono
```
### 5. Write your app
Only 4 lines!!
```js
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/', (c) => c.text('Hello! Hono!'))
app.fire()
```
### 6. Run
Run the development server locally. Then, access `http://127.0.0.1:8787/` in your Web browser.
```sh
$ wrangler dev
```
### 7. Publish
Deploy to Cloudflare. That's all!
```sh
$ wrangler publish
```
## Starter template
You can start making your application of Cloudflare Workers with [the starter template](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono-minimal). It is a realy minimal using TypeScript, esbuild, and Miniflare.
To generate a project skelton, run this command.
```
$ wrangler generate my-app https://github.com/yusukebe/hono-minimal
```
## Related projects
Implementation of the original router `TrieRouter` is inspired by [goblin](https://github.com/bmf-san/goblin). `RegExpRouter` is inspired by [Router::Boom](https://github.com/tokuhirom/Router-Boom). API design is inspired by [express](https://github.com/expressjs/express) and [koa](https://github.com/koajs/koa). [itty-router](https://github.com/kwhitley/itty-router), [Sunder](https://github.com/SunderJS/sunder), and [worktop](https://github.com/lukeed/worktop) are the other routers or frameworks for Cloudflare Workers.
- express
- koa
- itty-router
- Sunder
- goblin
- worktop
- Router::Boom
## Contributing
Contributions Welcome! You can contribute by the following way.
- Write or fix documents
- Write code of middleware
- Fix bugs
- Refactor the code
- etc.
Let's make Hono together!
## Contributors
Thanks to [all contributors](https://github.com/yusukebe/hono/graphs/contributors)!
## Author
Yusuke Wada
## License
Distributed under the MIT License. See [LICENSE](LICENSE) for more information.